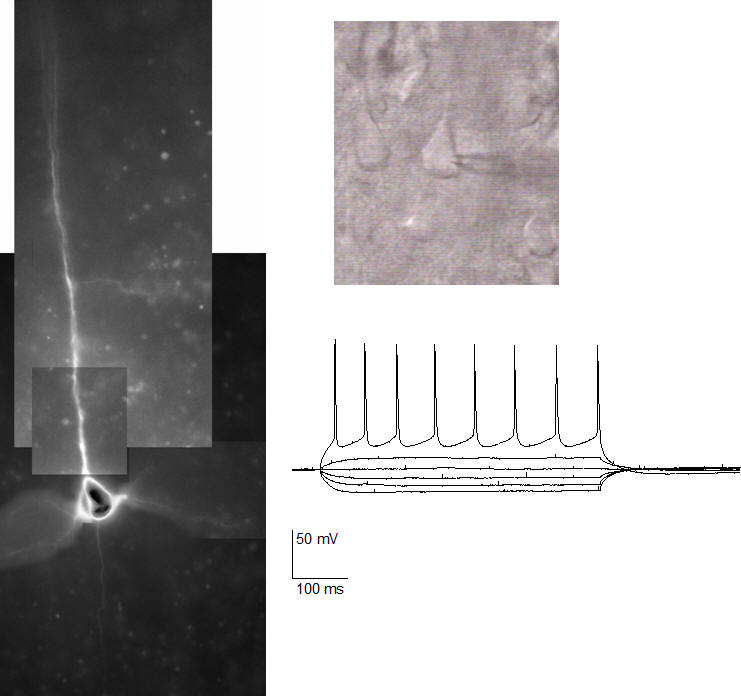
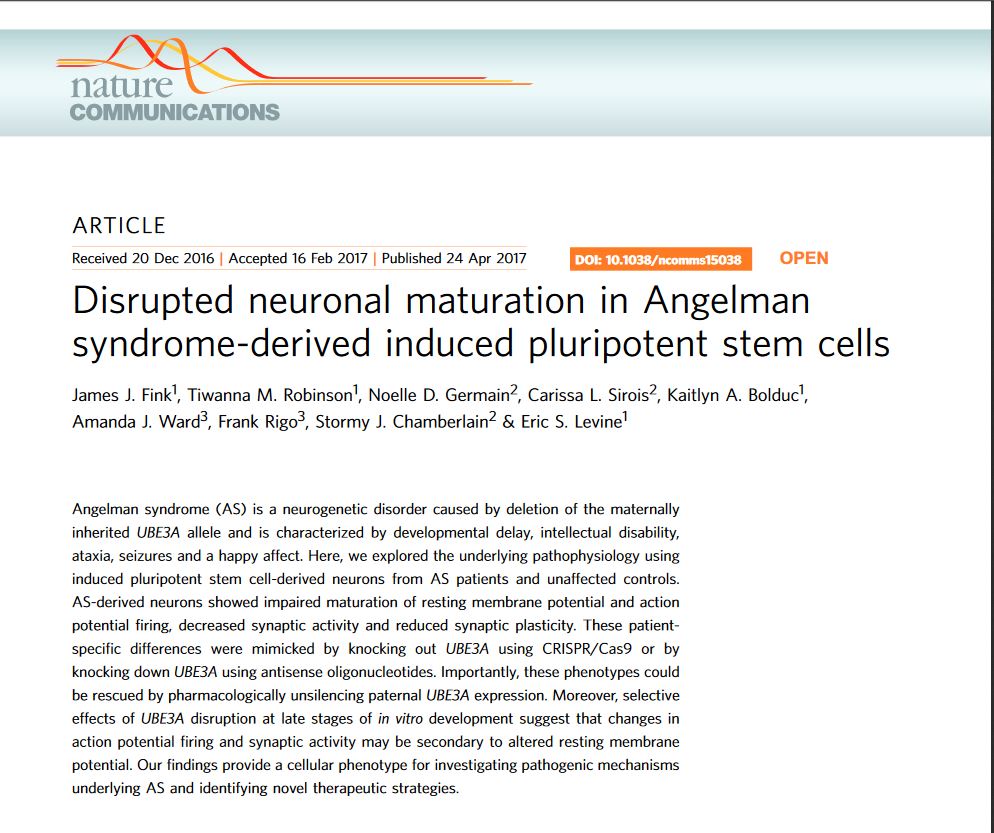
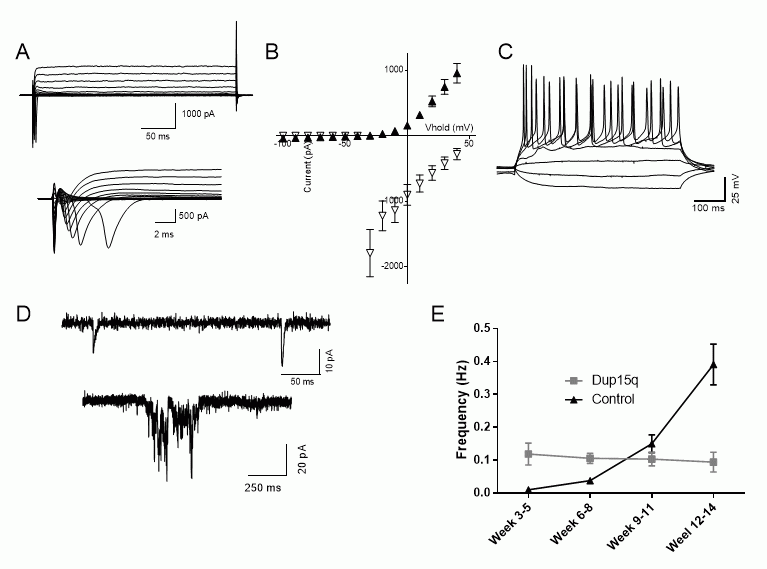
Induced pluripotent stem cell models of neurodevelopmental disease
We study forebrain neurons differentiated from patient-specific induced pluripotent stem cells to examine the cellular and synaptic pathophysiology in Angelman syndrome and dup15q autism.
BDNF and endogenous cannabinoid interactions in the neocortex and hippocampus
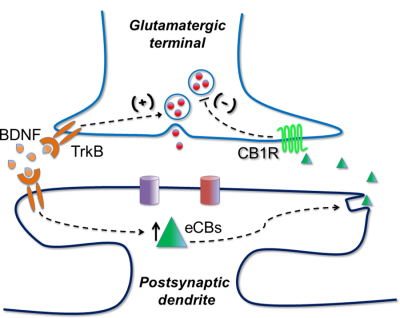
BDNF modulates presynaptic release probability at cortical glutamatergic synapses via opposing pre- and postsynaptic effects. BDNF activates presynaptic trkB receptors to directly enhance release probability, while simultaneously triggering the postsynaptic release of endocannabinoids that act to decrease release via presynaptic CB1 receptors.